Coronavirus crisis could see ‘a lost generation of vulnerable teenagers’ exploited by criminal gangs
The Children’s Commissioner has warned that the Covid-19 crisis has left thousands of teenagers at risk of “exploitation by gangs and organised criminals”.
Anne Longfield said the coronavirus lockdown could result in “a lost generation of teens” falling through the gaps in the school and social care system after months of school and college closures.
In her latest report she said even before the lockdown, 120,000 teenagers in England – around one in 25 – “were falling through gaps” in the school or social services systems.
“This puts them at increased risk of unemployment or of exploitation by gangs and organised criminals,” said Ms Longfield.
Her report highlights the risk of tens of thousands of teenagers “falling off the radar” through persistent absence from school, exclusions, alternative provision, dropping out of the school system in Year 11, or going missing from care.
She warns that those already “slipping out of sight” could be joined by many more who struggle to adapt to a return to ‘normal’ after six months out of school.
Unless these children are re-engaged in society, a whole generation of vulnerable teens could stay at risk of educational failure and unemployment, or crime or exploitation, said Ms Longfield.
“This summer I am particularly worried that teenagers who have finished year 11, who have seen their apprenticeship collapse, or have simply lost their way through lockdown, will simply fall off the radar,” she said. “Teenagers in colleges have so far been left out of catch-up funding.
“Many of these children, and I fear many thousands of other vulnerable teenagers, have had very little structure to their lives over the last six months. School was often a stretch for them, and I am concerned we are never going to get some of them back into education. If we do not act now, this could result in a lost generation of teens – dropping out of school, going under the radar, getting into trouble, and at risk of being groomed by gangs and criminals.
“We need to identify these children quickly and do whatever it takes over the summer to stabilise their lives and get them prepared for the structure of school again.
“We must not look back in five years at a generation of vulnerable teenagers who fell out of society and ended up drifting into crime and unemployment. They need extra help now as we emerge from lockdown.”

By September, schools will have been closed to most teenagers for half a year and children’s social care provision has also been curbed. The Children’s Commissioner is concerned that these teenagers, who were slipping through existing gaps in the system, will remain “invisible” even after the lockdown restrictions ease. These are children who are likely to have needs which schools struggle to meet but who often do not reach the threshold for social service involvement. It also comes at a time when youth services funding has been cut by 60 per cent over the past ten years, said Ms Longfield.
The report calls on councils to work with schools and police to focus resources on these teenagers at risk of becoming ‘invisible’ to services or who have gone missing under lockdown.
It says these children are “easy prey” to criminal gangs and are at very high risk of becoming ‘NEET’ (Not in Education, Employment or Training).
Ms Longfield says that ensuring they have a way of getting back into education, training or work is crucial for any economic recovery from Covid-19, and that many already vulnerable children who have been missing the structure that school brings will need extra support.
She is calling on the Government, schools, local authorities, police forces and safeguarding partnerships to work together on a plan to identify, track, support and ultimately re-engage these children.
The report also calls for summer schemes – including sports clubs, play schemes, holiday clubs and youth clubs – which give young people a range of safe, positive, structured activities to take part in, led by trusted adults and role models. To make this happen, the report says the Government must work with local areas to remove any barriers to delivering these schemes. It also calls on the Government to advise schools to support these schemes from within their additional £650 million ‘catch-up’ funding.
The report analyses data on all teenagers aged 13-17 who were on the radar of schools and children’s social care in 2017/18. It finds that 480,000 of these children had some kind of additional need, such as special educational need or disability (SEND), Child in Need (CIN) referral/episode, a fixed or permanent exclusion, high levels of school absence, or dropping out of school in Year 11. Around 100,000 of these teenagers were receiving high-cost statutory support, such as being in care, being on a child protection plan, having an education care and health plan or being enrolled at a Pupil Referral Unit (PRU).
The Children’s Commissioner is particularly concerned about the subset of these children who may not be getting the right level of help and may become removed from the systems intended to support them. She describes these children as “falling through the gaps” and defines this as children who:
- Have multiple CIN referrals during the year but do not end up on a CIN plan;
- Have SEND and also multiple exclusions from school during the year;
- Have a permanent exclusion but do not enter a PRU during the year;
- Are in care and living in an unregulated placement;
- Are in care and have multiple placement changes during the year;
- Have a permanent exclusion;
- Have high levels of unauthorised absence;
- Drop out of the school system in Year 11;
- Miss at least an entire term of school in the previous two years; and
- Are in care but go missing from their placement multiple times in a year.
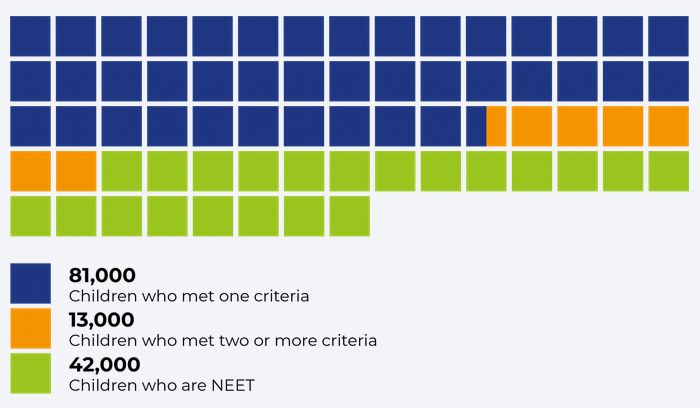
In 2017/18 around 81,000 teenagers in England met at least one of these criteria, including 13,000 who met two or more. On top of this, another 42,000 teenagers were NEET.
Adding these up, the report says there were 123,000 teens in England who were falling through gaps in mainstream provision and becoming invisible to services in 2017/18. This is four in every 100 teenagers aged 13-17 – around one in 25 teens.
The Local Government Association (LGA) said councils share the concerns of the Children’s Commissioner about the impact of the coronavirus crisis on vulnerable teenagers.
Councillor Judith Blake, chair of the LGA’s Children and Young People Board, said: “Councils are working with their partners and communities to try to identify children who may be at risk. As this report reinforces, it is vital that councils have the funding they need to support children, young people and families as part of the national recovery.”
Geoff Barton, general secretary of the Association of School and College Leaders, added: “Schools and colleges are acutely conscious of the risk that some pupils are vulnerable to drifting out of education, and they have worked very hard during the lockdown to check on these young people and keep them engaged.
“We would support any programme to provide extra support to help schools and colleges in this task over the coming months.”